Australian Education System

Schools
Each state in Australia manages and funds the school system within that state. There are both public and private schools in each state. While the curriculum may vary between states or schools, the areas of study are similar across the country.
Vocational Training
Australia has a Vocational Education and Training (VET) system that prepares people for work in occupations that do not require a university degree. The Australian Skills Quality Standards Authority (ASQA) manages the system, ensuring that national standards are maintained. Typically, a VET course lasts up to two years.
In the workplace, employers use learning outcomes and agreed courses to set training standards for employees. Many businesses also provide ongoing on-the-job training for employees. Some of this training can count towards formal qualifications.
Overseas graduates may have their qualifications recognised and may therefore be able to use them to seek employment.
Higher Education
The Australian federal government provides funding to universities in all states. Although each university operates independently and decides on its own courses and content, they are regulated by the Tertiary Education Quality and Standards Agency (TEQSA). Typically, a university course lasts three to four years.
Australian Qualifications Framework (AQF)
The Australian Qualifications Framework (AQF) is a system of 10 levels, divided into three areas:
School Education
Vocational Education and Training (TAFE)
Higher Education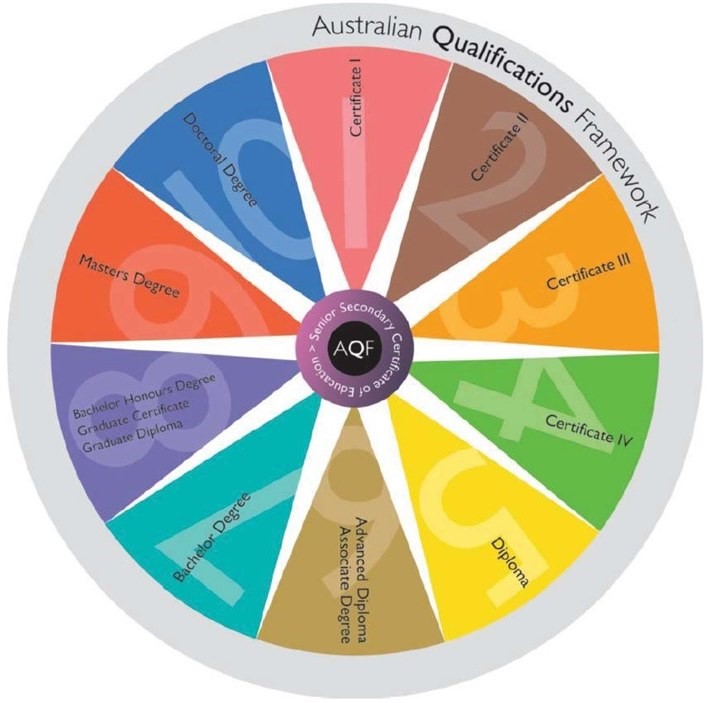
Level Type of qualification (English) Type of qualification (Vietnamese) Explanation
1 Certificate I Level 1 Certificate The most basic qualification, usually for those who are new to studying or working in a particular field.
2 Certificate II Level 2 Certificate A qualification that demonstrates more basic knowledge and skills than Level 1.
3 Certificate III Level 3 Certificate A general qualification, usually requiring knowledge and practical skills to work in a particular industry.
4 Certificate IV Level 4 Certificate A qualification that demonstrates more in-depth knowledge and the ability to work independently.
5 Diploma Higher Diploma A higher level qualification, usually requiring completion of a longer study programme.
6 Advanced Diploma Advanced Diploma A qualification that is more specialized than a Diploma, usually requiring a higher level of knowledge and practical skills. <br> Associate Degree
7 Bachelor Degree The most common undergraduate degree, requiring 3-4 years of study.
8 Bachelor Honors Degree A higher degree than a Bachelor Degree, usually requiring further research and writing a thesis. <br> Graduate Certificate
9 Master Degree A postgraduate degree, usually requiring independent research and writing a thesis.
10 Doctoral Degree The highest degree, requiring original research and new contributions to the field of study.
Source: https://www.aqf.edu.au/
Are all Australian education courses listed on the AQF?
Some courses are not listed on the AQF, even though they offer excellent education and outcomes. For example:
Many English Language Courses for Overseas Learners (ELICOS)
Some Foundation Studies
Other non-degree programs
These courses do not award formal qualifications as listed in the AQF table above.
Why is the AQF important?
The AQF is important because:
It provides a clear structure for the levels of each qualification.
It allows students to build their qualifications from low to high.
It allows one education provider to understand the level of a qualification offered by another and to award credits accordingly.
It helps international students to identify the right course, transfer to the right institution and transfer to the right level in accordance with the regulations and requirements of their student visa type.
Consulting contact information:
G2G Scholar Edu Company
Address (Australia): 28 Sutherland Street, Albanvale, VIC, 3021
Address (Vietnam): Goldsilk Complex, 430 Cau Am, Van Phuc, Ha Dong, Hanoi
Phone: +61474112375
Zalo: +84822301548
Email: admin@g2gedu.com.au








